Hey, Class 10 students! Welcome to your ultimate guide for Chapter 10: Light – Reflection and Refraction from the NCERT Science book. This chapter is all about how light behaves—like bouncing off mirrors or bending through water. It’s super important for your exams and really cool to understand! We’ll tackle the main questions with clear, easy answers to help you ace your studies. Let’s dive into the world of light!
What’s This Chapter About?
Light is everywhere—it lets us see the world! This chapter explores two big ideas: reflection (light bouncing back) and refraction (light bending). You’ll learn about mirrors, lenses, and how they work in daily life (think glasses or car mirrors). Let’s get to the questions!
Key Questions and Answers from Chapter 10
Here are the top questions from Light – Reflection and Refraction with simple, student-friendly explanations:
Q1: What is reflection of light?
Answer:
Reflection is when light hits a surface and bounces back.
- Law 1: Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r).
- Law 2: Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal (perpendicular line) lie in the same plane.
Example: You see yourself in a mirror—light reflects off it!
Q2: What are the types of mirrors? How do they work?
Answer:
- Plane Mirror: Flat, gives same-size, virtual images (e.g., bathroom mirror).
- Concave Mirror: Curves inward, can make real (upside-down) or virtual images (e.g., car headlights).
- Convex Mirror: Curves outward, makes small, virtual images (e.g., side mirrors).
Think: Concave = cave (focuses light), Convex = bulges out (spreads light).
Q3: What is the difference between real and virtual images?
Answer:
- Real Image: Formed where light rays meet, can be caught on a screen (e.g., cinema projector).
- Virtual Image: Rays don’t really meet, can’t be caught (e.g., mirror image).
Example: Concave mirror (close) = real; plane mirror = virtual.
Q4: What is the focal point and radius of curvature?
Answer:
- Focal Point (F): Where parallel rays meet (or seem to) after reflection/refraction.
- Radius of Curvature (R): Distance from mirror’s center to its curve—twice the focal length (R = 2F).
Example: In a concave mirror, light focuses at F, halfway to R.
Q5: What is the mirror formula? How do you use it?
Answer:
The mirror formula is:
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
- f: Focal length (positive for convex, negative for concave).
- u: Object distance (negative if in front).
- v: Image distance (positive for real, negative for virtual).
Example: u = -10 cm, f = -5 cm (concave).
1/-5 = 1/-10 + 1/v → 1/v = -1/5 + 1/10 = -1/10 → v = -10 cm (virtual image).
Q6: What is magnification in mirrors?
Answer:
Magnification (m) tells image size vs. object size:
m = h’/h = -v/u
- h’: Image height, h: Object height.
- Positive m = upright, negative = inverted.
Example: If v = -10 cm, u = -5 cm, m = -(-10)/-5 = 2 (twice as big, upright).
Q7: What is refraction of light?
Answer:
Refraction is when light bends as it moves between mediums (e.g., air to water).
- Cause: Light slows down or speeds up (e.g., slower in glass).
- Law 1: Incident ray, refracted ray, and normal are in one plane.
- Law 2: Snell’s Law—n₁ sin i = n₂ sin r (n = refractive index).
Example: A pencil in water looks bent—refraction tricks your eyes!
Q8: What is the refractive index?
Answer:
Refractive index (n) measures how much light bends:
n = Speed of light in vacuum (c) / Speed in medium (v).
- Example: n of water = 1.33 (light slows 1.33 times).
Use: Higher n = more bending (e.g., glass > water).
Q9: What are lenses? Name their types.
Answer:
Lenses bend light to form images:
- Convex Lens: Thicker in the middle, converges light (e.g., magnifying glass).
- Concave Lens: Thinner in the middle, diverges light (e.g., some eyeglasses).
Think: Convex = “converge,” Concave = “cave away.”
Q10: What is the lens formula?
Answer:
The lens formula is:
1/f = 1/v – 1/u
- f: Focal length (positive for convex, negative for concave).
- u: Object distance (negative).
- v: Image distance (positive for real, negative for virtual).
Example: u = -15 cm, f = 10 cm (convex).
1/10 = 1/v – 1/-15 → 1/v = 1/10 – 1/15 = 1/30 → v = 30 cm (real image).
Q11: What is the power of a lens?
Answer:
Power (P) measures lens strength:
P = 1/f (f in meters).
- Unit: Dioptre (D).
- Convex = positive P, Concave = negative P.
Example: f = 0.5 m → P = 1/0.5 = +2 D (convex).
Q12: Why does a straw look bent in water?
Answer:
Light from the straw bends as it moves from water (n = 1.33) to air (n = 1). The part in water seems higher than it is—refraction creates the illusion!
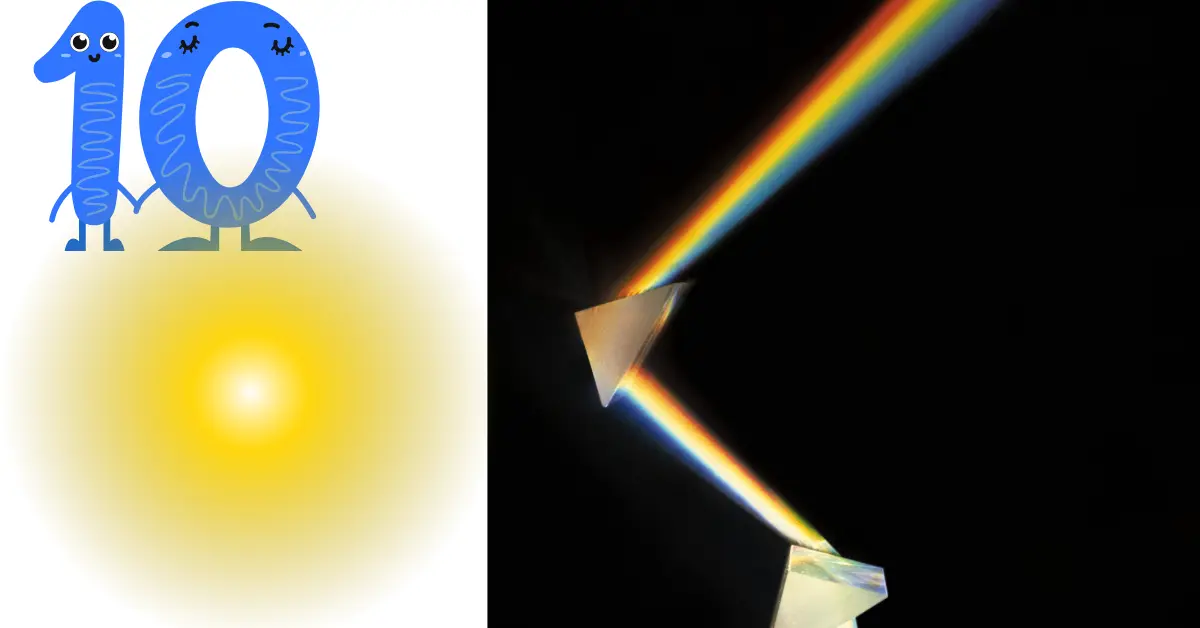
Q13: What happens when light passes through a glass prism?
Answer:
Light bends twice (entering and exiting), splitting into colors (dispersion).
- Why: Each color has a different speed in glass (red fastest, violet slowest).
Result: Rainbow pattern—red on top, violet at bottom.
Q14: How do concave and convex mirrors differ in image formation?
Answer:
- Concave: Real, inverted (object beyond F); virtual, upright (object between F and mirror).
- Convex: Always virtual, upright, smaller.
Example: Concave in shaving mirrors (big image), convex in traffic mirrors (wide view).
Q15: Why do we see a magnified image with a convex lens?
Answer:
When an object is between F and 2F of a convex lens, light converges to form a larger, real image on the other side.
Use: Magnifying glass—try it with tiny text!
Extra Questions from NCERT Exercises
- What is the sign convention for mirrors?
Answer: Left of pole = negative (u, f for concave), right = positive (v for real). - Why does a convex mirror never form a real image?
Answer: It diverges light—rays never meet in front. - How does a convex lens act as a burning glass?
Answer: Focuses sunlight to a tiny, hot spot (focal point).
Tips to Master Chapter 10
- Learn Ray Diagrams: Draw plane, concave, convex mirrors/lenses—practice 5 each!
- Memorize Formulas: Mirror, lens, power—write them daily.
- Understand Signs: Negative u, positive/negative f—get it clear.
- Relate to Life: Mirrors in cars, lenses in glasses—see it around you!
- Solve Numericals: Practice 5 problems daily (e.g., find v, m).
Chapter 10: Light – Reflection and Refraction is like unlocking the magic of light—how it bounces, bends, and shapes what we see. With these questions and answers, you’re all set to shine in your Class 10 Science exams! Keep practicing, stay curious, and you’ll nail it. Got doubts? Drop them below—I’m here to help. Happy studying, light wizards!
Also Read: Active and Passive Voice: Examples with Answers for Class 10
1 thought on “Class 10 Science Chapter 10: Light – Reflection and Refraction – Questions and Answers Made Simple”